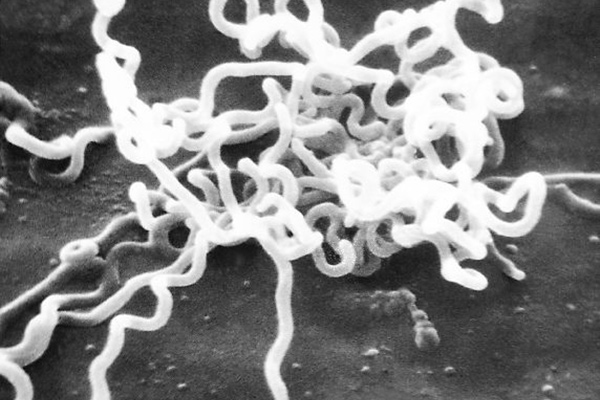
Syphilis
4. Februar 2022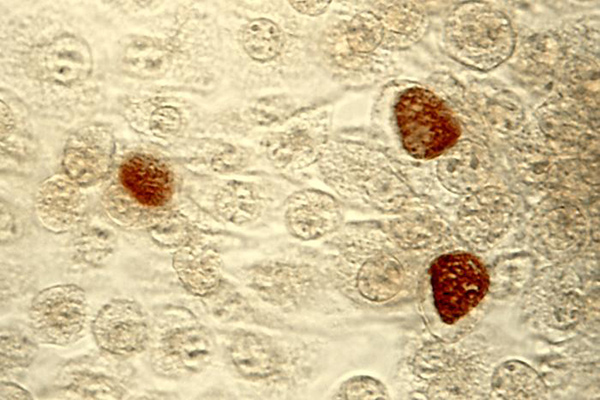
Chlamydien
8. Februar 2022Tripper (Gonorrhö)
Ein Tripper ist – gemeinsam mit Chlamydien – eine der am häufigsten auftretenden sexuell übertragbaren Infektionen. Die Gonokokken-Bakterien können leicht übertragen werden und befallen meist die Schleimhäute von Rachen, Enddarm oder Harnröhre.
Übertragung
Gonokokken lassen sich bei fast allen Sexpraktiken übertragen, bei denen es zu direktem Kontakt von (infizierten) Schleimhäuten kommt.
Ein Tripper ist leicht übertragbar. Nicht nur beim Ficken, sondern auch beim Blasen, Lecken, Rimming, Fisten, gegenseitigem Wichsen und intensivem Küssen können die Bakterien weitergegeben werden. Außerhalb der menschlichen Schleimhaut sterben die Bakterien jedoch schnell ab (deshalb ist beispielsweise eine Übertragung über Toilettensitze nicht möglich).
Schutz
- Kondome und interne Kondome können das Risiko einer Infektion reduzieren. Diese kannst Du auch verwenden, um eine Übertragung durch geteilte Toys zu reduzieren.
- Beim Fisten oder Fick mit mehreren Partner*innen: Wechsel das Kondom, die Handschuhe oder das Toy, bevor du jemand anderes fickst.
- Achte auf deinen Schutz vor HIV. Bei einer Tripper-Infektion kann das Risiko einer HIV-Übertragung steigen, da das HI-Virus durch die Entzündungen und die damit verbundene Schädigung der Schleimhäute einen einfacheren Weg in den Körper findet.
- Bei Menschen mit unbehandelter HIV-Infektion, die eine durch Gonokokken hervorgerufene Entzündung des Gebärmutterhalses, des Enddarms oder der Harnröhre haben, ist das Risiko einer HIV-Übertragung auf andere erhöht, weil entzündete Schleimhaut und Entzündungssekrete besonders viele Viren enthalten – auch „Huckepack-Infektion“ genannt.
- Regelmäßige Tests helfen, eine Infektion frühzeitig zu erkennen und schnellstmöglich zu behandeln.
- Informiere deine Sexpartner*innen und warte das Ende der medizinischen Behandlung ab, bevor Du wieder Sex hast.
Symptome
Häufig verursacht ein Tripper keine oder undeutliche Beschwerden. Dadurch wird die Infektion oft spät erkannt und behandelt. In manchen Fällen führt eine unbehandelte Infektion zu Unfruchtbarkeit.
Tripper an Geschlechtsorganen und / oder Harnröhre
- Nach ca. drei Tagen können Jucken, Brennen und Eiter auftreten.
- Ausfluss aus dem Schwanz (gelb, milchig und meist übelriechend), auch „Bonjour-Tropfen“ genannt.
- Schmerzende Entzündung der Prostata oder Nebenhoden möglich.
- Im Samenleiter können narbige Verklebungen zu Zeugungsunfähigkeit führen.
Der Tripper kann zwar von alleine abheilen, aber auch chronisch werden. Die Erreger können dann weiterhin auf andere übertragen werden und sich im Körper ausbreiten.
Tripper im Arsch und / oder Rachen
- Häufig symptomlos
- Jucken, Brennen
- Schmerzen beim Ficken
- Schleimige Beimengen beim Stuhlgang
- Halsschmerzen
Die Erreger beim Tripper im Rachen verschwinden in der Regel nach einiger Zeit von selbst.
Test & Behandlung
Ein Tripper kann über einen Abstrich oder mit Hilfe einer Urinprobe festgestellt werden und ist mit Antibiotika gut heilbar.
Die Tests können bei Ärzt*innen der Urologie oder für Haut- und Geschlechtskrankheiten gemacht werden. In vielen Zentren für sexuelle Gesundheit, Aidshilfen oder Testprojekten wie Checkpoints werden die Tests und Beratungen oft anonym und kostengünstig angeboten.
Weitere Informationen bietet die Deutsche Aidshilfe hier.
